Policy
FIACCT 02-11_01 General accounting- System access-digital certificate
Effective: April 5, 1999
Revised: September 1, 2006
Reviewed:
Purpose
This policy establishes guidelines for requesting and obtaining a registered digital certificate from Digital Signature Trust (DST) for use with Finance applications transmitting private data through e-mail or Internet browser applications.
Background
In order to provide assurance that parties who communicate are “safe,” e.g., their identities are valid and trustworthy, and to have the ability to encrypt data that is e-mailed or transmitted over the Web, Finance is implementing a public-key infrastructure (PKI) to manage keys and certificates. A PKI is a comprehensive system to provide data encryption and digital signature services.
The difference between digitally signing and encrypting is this: Digitally signing a message means you attach your Digital ID to it so that the recipient knows it came from you and was not tampered with en route. Signing authenticates a message, but it does not provide protection against third-party monitoring. Encrypting a message means you “scramble” it in a way that only the intended recipient can “unscramble” it, which safeguards against third-party monitoring.
In order to send a signed message, you must have a Digital ID (also known as digital signature or digital certificate). To provide a “safe” identity, authorized users will be issued a registered digital certificate from DST through the Finance security administrator. The certificate issuance provides the authorized user with a unique set of digitized information which belongs only to the registered user and identifies him or her to the specified Finance application.
To encrypt data for e-mailing, Finance has selected ENTRUST software. The digital certificate information is imported into the ENTRUST software. Encryption software uses a matched pair of encryption and decryption keys named a Public Key and a Private Key. A public key and private key, the Key Pair, are created for a certificate holder at the time the digital certificate is issued. Each key performs a one-way transformation upon the data. Each key is the inverse function of the other; what one does, only the other can undo. They are mathematically related in that the private key is required to invert operations performed with the public key, and the public key is required to invert operations performed with the
private key.
Encrypting a message for a specific recipient requires that you have the portion of the recipient’s digital certificate called the Public Key. The Public Key is made publicly available by its owner, while the Private Key is kept secret and secure by its owner. To send a private message, an author scrambles the message with the intended recipient’s Public Key. Once so encrypted, the message can be decoded only with the recipient’s Private Key. Inversely, the owner can also scramble data using the Private Key; in other words, keys work in either direction. This provides the basis for the digital signature, since if the user can unscramble a message with someone’s Public Key, the other user must have used their Private Key to
scramble it in the first place. Since only the owner can utilize their own Private Key, the scrambled message becomes a kind of electronic signature—a document that nobody else can produce.
Each Digital ID specifically verifies that your public key is bound to your stated e-mail address, so each e-mail address requires its own ID. Finance e-mail software uses S/MIME (Secure/ Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) protocol for sending secure mail over the Internet. MIME is the industry’s standard format for electronic mail which defines how the body of a message is structured. S/MIME adds digital signatures and encryption to that format. This standardization of format allows users with different e-mail software to communicate with one another. In order to send and receive secure e-mail using a Digital ID, you must be working with e-mail software that supports S/MIME.
Security Issues
The security of encrypted messages relies on the security of the private key, which must be protected against unauthorized use. A key pair is bound to a user’s name and other identifying information and functions as electronic credentials that can be checked when membership or services restrict access to particular users.
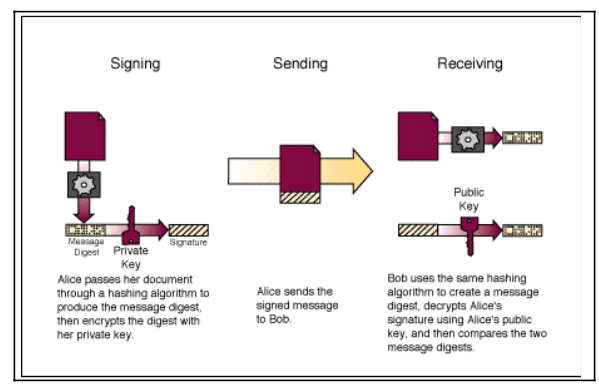
A digital signature functions for electronic messages like a handwritten signature does for printed documents. The signature is an unforgeable piece of data which asserts that a named person wrote or otherwise agreed to the information to which the signature is attached. A digital signature actually provides a greater degree of security than a handwritten signature because the signer of the document cannot later disown it by claiming the signature was forged. Once a key is generated, it must remain secret to avoid unfortunate mishaps (such as impersonation). If an intruder can obtain a private key, the intruder can impersonate another user. If someone’s private key is lost or compromised, others must be made aware of this, so they will no longer encrypt messages under the invalid public key nor accept messages signed with the invalid private key. Users must store their private keys securely, so no intruder can obtain them.
Each certificate owner must accept personal responsibility for the security of their private key. The key must be password protected and it is recommended that the computer on which the key resides also be password protected. If the computer is exchanged with another, the user should copy the private key to a diskette, delete it from their hard drive, and reinstall and password protect the key on the new computer. If the user changes jobs and or responsibilities and the private key is no longer needed, the user should take responsibility for the revocation of the certificate issued to them.
Policy
A. Each manager who has an employee needing to send or receive Finance private data through e-mail or the Internet must complete and submit the appropriate security request form (SA 9, Digital Signature Request Form) to obtain a digital certificate. The submitted form must be the correct and/or updated version and must be completed in its entirety before the manager’s application for the employee will be processed.
B. It is the manager’s responsibility to complete the SA 9, Digital Signature Request Form, and submit the form to their agency security administrator for signature. The agency security administrator will validate the information, sign the form, and forward it to the Finance security administrator for processing. If the agency does not have a security administrator, the manager should work directly with the Finance security administrator.
C. It is the manager’s responsibility to notify the security administrator(s) of any change in an employee status affecting the employee’s official job function related to the use of the digital certificate to prevent unauthorized use of the digital certificate. The digital certificate is issued to the employee and should be immediately revoked when no longer needed by that employee.
D. The Finance security administrator reserves the right to initiate necessary steps to revoke the certificate should either of the following policy violations occur:
1. Any manager fails to notify Finance of employee status changes.
2. Someone other than the certificate subscriber is using the digital certificate.
Access will be granted on a need-to-know basis as part of the employee’s official job function
Procedures
Responsibility
Manager
Action
Complete the security SA 9, Digital Signature Request Form, to request a digital certificate. Sign and return the form to the agency security administrator. Include a purchase order number or a purchasing card number for the ENTRUST client software and the issuance of the digital certificate.
Agency Security Administrator
Verify the information and forward the form to the Finance Security Administrator.
Finance Security Administrator
Obtain the application manager’s approval signature. Forward the completed information to DST for certificate issuance.
DST
Generate the Key Pair and issue the digital certificate. Send the Certificate and keys to the authorized user. Send the client copy of ENTRUST software to authorized users. Notify Finance of completed status.
Authorized User
Install the ENTRUST client software. Install and password protect the certificate on the computer hard drive. E-mail Finance a non-encrypted message containing your public key.
Notify your agency security administrator and Finance Security Administrator of any compromises in the security of the private key or any changes in status affecting the use of the key.